Microneedling vs. Chemical Peels for Melasma Treatment
- ghulamabbas7474614
- Jul 12, 2025
- 4 min read
Melasma—a common and often stubborn skin pigmentation issue—can be challenging to manage. Those dealing with this condition are frequently searching for effective solutions. Two of the most buzzed-about treatment options today are microneedling and chemical peels. But which one is more effective? And more importantly, does microneedling help with melasma?
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of these treatments, their processes, benefits, side effects, and post-care instructions. Whether you're considering one of these for yourself or just gathering insights, keep reading for a detailed guide that’s designed for human readers and optimized for Google crawling and indexing.
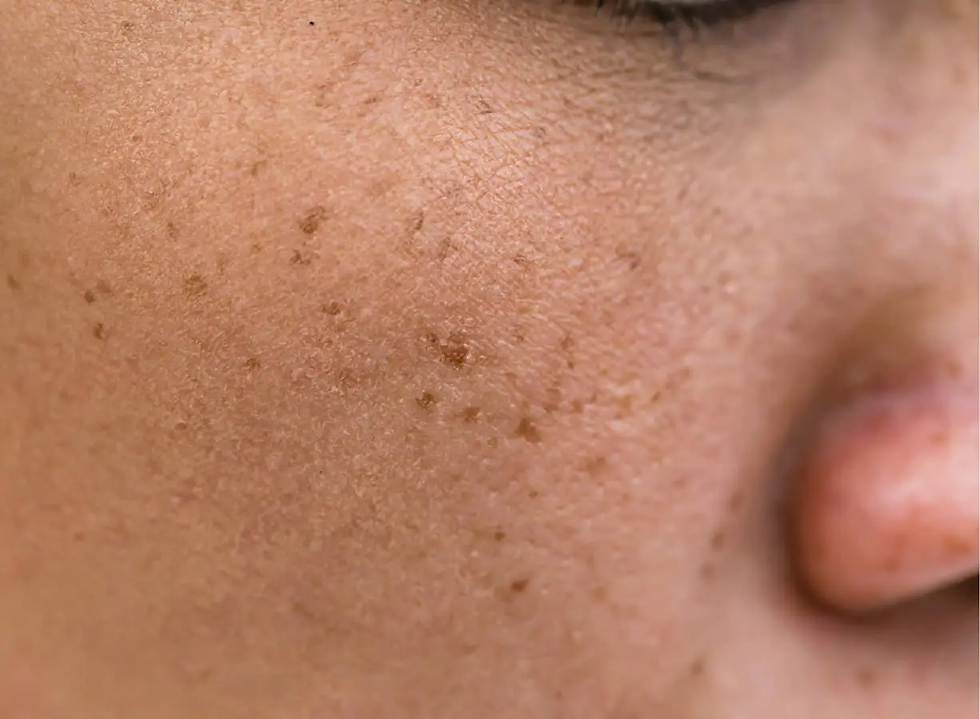
Understanding Melasma: What You’re Dealing With
Before diving into treatments, it’s important to understand what melasma actually is. Melasma appears as dark, irregular patches typically on the face—especially the cheeks, upper lip, forehead, and chin. It’s most common in women, particularly during hormonal changes like pregnancy or birth control use.
Although harmless, melasma can significantly affect confidence. This is why people seek effective treatment options like microneedling and chemical peels.
What is Microneedling?
Microneedling, also known as collagen induction therapy, involves creating controlled micro-injuries in the skin using fine needles. These micro-wounds stimulate the body's natural wound-healing processes, which boosts collagen and elastin production.
But does microneedling help with melasma? According to several dermatological studies and real-world clinical results, yes—microneedling has been shown to reduce the appearance of melasma by enhancing the absorption of topical lightening agents and encouraging cellular regeneration.
Benefits of Microneedling for Melasma
Enhanced absorption of serums like tranexamic acid or vitamin C
Minimal downtime compared to invasive treatments
Safe for darker skin tones, where chemical peels might increase risks of hyperpigmentation
Long-term collagen boost improves overall skin texture and tone
What are Chemical Peels?
Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution (such as glycolic acid, lactic acid, or trichloroacetic acid) to exfoliate and eventually peel off the top layers of the skin. This reveals newer, more even-toned skin underneath.
Chemical peels are available in various intensities—superficial, medium, and deep—depending on the depth of skin targeted.
Benefits of Chemical Peels for Melasma
Quick exfoliation of pigmented skin
Stimulates skin turnover
Can be combined with other topical agents for enhanced results
Effective for epidermal melasma, where pigmentation lies in the top layer of the skin
Microneedling vs. Chemical Peels: Head-to-Head Comparison
Category | Microneedling | Chemical Peels |
Mechanism | Collagen induction + serum absorption | Exfoliation via acid-induced skin peeling |
Ideal For | Dermal or mixed melasma, sensitive/darker skin types | Epidermal melasma, fairer skin types |
Downtime | 1–3 days of redness/swelling | 3–7 days of peeling, redness, sensitivity |
Side Effects | Minor swelling, pinpoint bleeding | Flaking, peeling, post-inflammatory pigmentation |
Cost | Typically higher due to needling device and topical serums | Generally lower; price varies by peel depth |
Skin Tone Suitability | Safe for all skin tones with proper technique | May pose risk of PIH (Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation) in darker skin tones |
Keyword Benefit | Does microneedling help with melasma? — YES, by improving absorption and skin renewal | Less effective for deeper pigmentation, though still widely used |
Post-Treatment Care: Microneedling vs. Chemical Peels
Regardless of your choice, post-treatment care is critical for maximizing results and avoiding complications.
After Microneedling
Avoid sun exposure for at least 48 hours
Use a gentle, non-active cleanser
Moisturize and hydrate frequently
Apply sunscreen (SPF 50+), even indoors
Avoid makeup for at least 24 hours
After Chemical Peels
Do not pick or peel flaking skin
Use bland moisturizers and cleansers
Avoid exfoliants, acids, or retinoids for 1–2 weeks
Apply sunscreen religiously to avoid further pigmentation
Who Should Choose Microneedling?
If you’re asking, Does microneedling help with melasma?, and especially if you have darker skin or mixed melasma (both dermal and epidermal), microneedling may be your better option. The treatment offers steady improvement with lower risks of pigmentation rebound, particularly when paired with lightening agents like tranexamic acid or niacinamide.
Who Should Consider Chemical Peels?
If you have fair to medium-toned skin and superficial (epidermal) melasma, chemical peels might offer faster visible results. However, the deeper the peel, the more risk and downtime are involved. Mild peels done regularly are often safer and just as effective over time.
Combining Treatments for Better Results
In many dermatology clinics, microneedling and chemical peels aren’t an either/or decision—they’re used in combination. A popular protocol involves microneedling followed by topical tranexamic acid for deep melasma, and light chemical peels in-between sessions for surface brightening.
Consulting a qualified dermatologist can help customize a treatment plan based on:
Skin type
Depth of pigmentation
Past treatment response
Budget and availability for downtime
Risks & Considerations
Both treatments carry minimal risks when performed by licensed professionals. However, improper technique, poor aftercare, or pre-existing skin conditions can lead to:
Worsened pigmentation
Scarring
Infection
That’s why it’s important to always choose certified and experienced providers who understand your skin type and melasma behavior.
Final Verdict: Which One Is Better?
There’s no one-size-fits-all answer. However, if you’re still wondering Does microneedling help with melasma?, the evidence leans toward yes, especially when used correctly and consistently. Chemical peels also remain a strong contender, particularly for surface-level pigmentation.
In general:
Choose microneedling for deeper pigmentation, sensitive or dark skin, and longer-term skin regeneration.
Opt for chemical peels for lighter pigmentation, quicker results, and fairer skin.
Conclusion: Treating Melasma the Smart Way
Melasma can be persistent, but not untreatable. Whether you lean toward microneedling or chemical peels, understanding the science behind both is key. The question Does microneedling help with melasma? has a clear, research-backed answer—yes, when done right. But even then, consistency, proper aftercare, and professional guidance remain your best tools for success.
For best results, consult with a dermatologist to create a plan tailored to your skin’s unique needs. With the right treatment approach, even the most stubborn melasma can fade into a more even, radiant complexion.



Comments